Hello, tis me, the human with a maths GCSE, ready to explain Pythagoras’ Theorem :]
Pythagoras’ Theorem is the mathematical formula used to calculate the lengths of sides in right angled triangles.
Using this theorem, you can figure out the sides of any right-angled triangle, provided that you know two of the other sides.
The formula is:
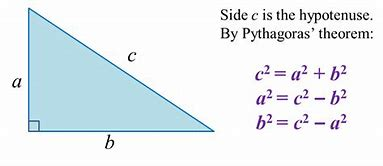
a^2+b^2=h^2
(^2 means squared)
‘a’ represents one side of the right angled triangle, adjacent (next to) the right angle.
‘b’ represents the other side of the triangle, next to the right angle.
(it doesn’t matter which order these go in)
‘h’ (sometimes called ‘c’) represents the hypotenuse, which is a fancy term for the line directly across from the right angle.
Here’s a diagram:
As shown above, you can rearrange your formula for whichever side you need to find.
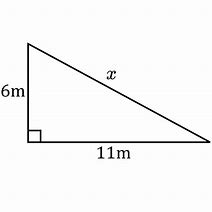
Example:
So, we know 6^2+11^2=x^2
(I’m gonna bring x to the right cus it makes it easier for me):
x^2=6^2+11^2
6^2 = 36
11^2 = 121
36+121=157
That means:
x^2=157
But we are not finished yet
To find ‘x’, we simply find the square root of 157, meaning:
x = 12.5299641
If you have any questions or are stuck with any problems, comment them below!
@Students